When pain strikes during a morning jog or weekend game, how do doctors pinpoint the exact source of the problem? Traditional methods like physical exams or X-rays often leave gaps in understanding soft tissue health. That’s where advanced technology steps in.
Modern diagnostic tools use magnetic fields and radio waves to create crystal-clear pictures of bones, tendons, and connective tissues. This approach helps medical teams spot issues invisible to other scanning methods. We’ll walk you through how this process works—from pre-scan routines to decoding results.
Our guide simplifies complex medical concepts for both patients and professionals. You’ll discover why this imaging method outperforms alternatives for detecting subtle damage. We’ll also explain how preparation impacts scan quality and what different result patterns mean for recovery plans.
Key Takeaways
- Advanced imaging reveals hidden joint issues traditional methods miss
- Non-invasive scans provide detailed views of soft tissues and bone structures
- Proper preparation ensures clearer results and more accurate diagnoses
- Understanding scan reports helps shape effective treatment strategies
- Comparison with other imaging options highlights unique advantages
Understanding the Role of MRI in Diagnosing Knee Ligament Injuries
Cutting-edge technology allows medical teams to visualize structures hidden beneath the skin’s surface. Unlike basic imaging methods, modern systems create multi-layered views of connective tissues, cartilage, and fluid patterns. This precision helps identify subtle abnormalities that physical exams might overlook.
The Science Behind Detailed Scans
Magnetic resonance imaging uses powerful magnets and radio waves to map hydrogen atoms in the body. When these atoms respond to energy pulses, they emit signals processed into high-resolution cross-sections. This approach captures even minor swelling or micro-tears in fibrous bands.
Imaging Options Compared
Different tools serve unique purposes in diagnostics. X-rays excel at showing bone fractures, while CT scans combine multiple angles for 3D bone analysis. Magnetic resonance scans, however, provide unmatched clarity for:
- Cartilage wear patterns
- Fluid accumulation around joints
- Partial or complete fiber disruptions
| Modality | Best For | Soft Tissue Detail | Radiation |
|---|---|---|---|
| X-Ray | Bone fractures | Low | Yes |
| CT Scan | Complex bone breaks | Moderate | High |
| Resonance Imaging | Ligaments & cartilage | High | None |
Specialized techniques like oblique-angle captures further enhance diagnostic accuracy. These methods adjust scan planes to match natural tissue orientations, reducing blind spots in standard views.
Preparing for Your Knee MRI Procedure
Your journey to precise diagnostics starts with smart preparation. We guide patients through essential steps to ensure their scan delivers maximum clarity while prioritizing comfort. Proper planning reduces delays and helps technicians capture the detailed images doctors need.
What to Expect Before and During the Scan
Most facilities recommend wearing athletic shorts or loose pants without metal fasteners. You’ll remove jewelry, watches, and other accessories before entering the scanning room. The procedure typically takes 20-45 minutes, depending on the complexity of your case.
Technologists often provide ear protection to muffle the machine’s rhythmic tapping sounds. Staying completely still during image capture prevents blurry results. Some clinics use cushions or straps to help maintain proper positioning throughout the session.
Safety Precautions and Metal-Free Guidelines
Metal objects pose serious risks in strong magnetic fields. Inform your care team about dental work, surgical implants, or piercings beforehand. Even makeup with metallic particles should be avoided.
We emphasize three critical safety checks:
- Empty pockets of coins, keys, and magnetic cards
- Remove removable dental devices
- Disclose any electronic implants or metal fragments in your body
Clear communication with your medical team helps prevent scan cancellations. Patients with anxiety can request relaxation techniques or discuss alternative options with their provider.
MRI for knee ligament injuries: What You Need to Know
Proper preparation transforms medical scans from daunting to routine. Our team guides patients through essential steps that enhance both safety and result clarity. Following these protocols helps technicians capture precise views of complex joint structures.
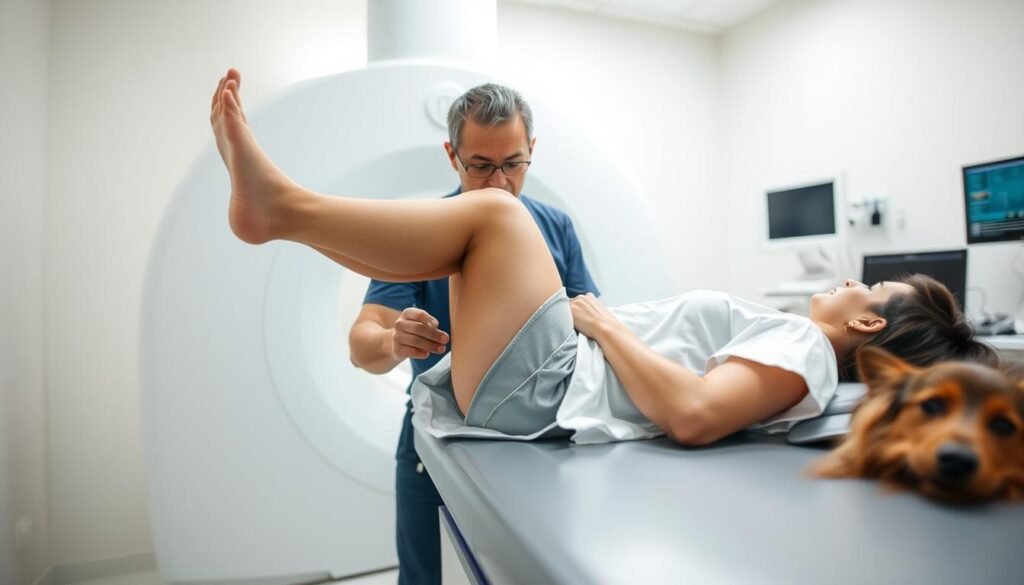
Pre-Scan Considerations and Patient Preparation
Clothing choices matter more than many realize. Facilities typically provide gowns to eliminate zippers or metallic threads that distort images. We recommend arriving early to complete safety paperwork and discuss any implanted devices with technicians.
Three critical preparation steps ensure accurate results:
- Remove all jewelry and accessories
- Confirm no metallic cosmetics were applied
- Disclose recent surgeries or foreign objects
Positioning and Scan Duration Explained
Technologists position patients lying flat with the affected joint centered in the scanner. Foam pads gently immobilize the area while allowing natural breathing. This alignment helps create distortion-free cross-sectional views.
Standard evaluations take 25-35 minutes, though complex cases may require longer sessions. Factors extending scan time include:
- Need for contrast agents
- Multiple imaging sequences
- Patient movement requiring retakes
Clear communication helps manage expectations throughout the test. Our staff explains each machine noise and progress update, turning clinical procedures into collaborative experiences.
Interpreting MRI Results in Knee Ligament Diagnosis
Decoding medical images requires both expertise and precision. Radiologists analyze cross-sectional views to map tissue integrity while distinguishing between normal variations and trauma markers. This process transforms raw data into actionable insights for treatment planning.
Identifying Ligament Tears and Other Injuries
Complete ruptures appear as discontinuous fibers with fluid-filled gaps. Partial damage shows frayed edges or localized swelling. Key indicators include:
- Abnormal signal intensity in fibrous bands
- Fluid accumulation around joint structures
- Distorted anatomical alignment
| Injury Type | MRI Appearance | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Complete Tear | Black line disruption | Surgical evaluation needed |
| Partial Tear | Grayish fiber thickening | Physical therapy focus |
| Sprain | Fuzzy tissue margins | Rest and monitoring |
Overcoming Challenges in Reading Complex Knee Images
Overlapping tendons and scar tissue can mimic damage patterns. Experienced specialists use multi-planar reconstructions to separate adjacent structures. “We compare multiple sequences to confirm findings,” notes Dr. Ellen Torres, musculoskeletal radiologist.
Three strategies improve diagnostic accuracy:
- Correlating imaging with physical exam results
- Using specialized software for 3D modeling
- Reviewing prior scans for baseline comparisons
Subtle signs like micro-hemorrhages require high-resolution coils and optimized scan protocols. When uncertainties persist, multidisciplinary teams combine imaging data with patient history to reach consensus.
Advanced Imaging Techniques in Multi-Ligament Knee Injuries
Modern medicine solves complex diagnostic puzzles through innovative scanning approaches. Recent advancements help specialists visualize overlapping structures that standard methods might miss, particularly in cases involving multiple damaged areas.
The Role of Oblique Views in Detailed Assessments
Angled scanning planes now complement traditional imaging methods. By aligning with natural tissue orientations, these specialized views reveal hidden damage patterns. A 2023 Johns Hopkins study found oblique captures improved diagnostic confidence by 38% in complex cases.
Technologists achieve these perspectives by tilting the scanner’s magnetic field. This technique separates intertwined fibers in:
- Crisscrossing connective bands
- Multi-directional support tissues
- Layered joint stabilizers
Enhanced clarity reduces guesswork during radiologist exams. One patient’s scan initially showed ambiguous findings, but oblique sequences clearly identified a partial tear needing targeted therapy. Such precision directly impacts treatment roadmaps.
Ongoing software upgrades continue refining image quality. As resolution improves, so does our ability to match scan findings with surgical observations. These developments underscore technology’s vital role in advancing patient care.
Integrating Clinical Findings with MRI Imaging Insights
Accurate diagnosis requires more than advanced scanners. We combine physical examination results with detailed imaging data to paint complete clinical pictures. This dual approach catches subtleties either method might miss alone.
Recent clinical studies show 27% of complex cases require both approaches for proper assessment. Physical tests reveal joint stability issues, while scans map internal damage patterns. Together, they answer critical questions about injury severity and healing potential.
| Aspect | Clinical Exam | Imaging Insights |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Scope | Functional limitations | Structural abnormalities |
| Detail Level | Surface observations | 3D tissue analysis |
| Functional Assessment | Real-time movement tests | Static position snapshots |
Three key limitations of isolated imaging emerge in practice:
- Cannot assess pain responses during movement
- May miss transient instability episodes
- Requires anatomical knowledge for proper interpretation
In one recent case, a patient’s scans appeared normal despite persistent swelling. Physical tests revealed instability, prompting targeted therapy that prevented further damage. Such integrated evaluations help avoid both under-treatment and unnecessary procedures.
“The best outcomes occur when we treat patients, not just images.”
Our team coordinates with surgeons and therapists to align findings with treatment options. This collaboration ensures recovery plans address both visible damage and functional needs.
How MRI Informs Treatment Decisions for Knee Injuries
Clear diagnostic insights transform uncertain situations into actionable plans. Medical teams analyze detailed body scans to map damage severity and chart precise recovery roadmaps. This approach helps match treatment intensity to each patient’s unique needs.
Strategic Care Selection Through Visual Evidence
Scans reveal what physical exams can’t detect. Complete fiber tears often require surgical repair, while partial damage might heal with targeted therapy. A 2023 Mayo Clinic study found imaging guidance reduced unnecessary procedures by 41%.
Key factors influencing treatment choices:
- Tissue integrity shown in cross-sectional views
- Fluid patterns indicating inflammation levels
- Alignment of joint structures during rest
Bridging Physical Tests and Digital Proof
We combine hands-on assessments with scan data to validate findings. A stable joint during movement tests might override minor image abnormalities. Conversely, hidden damage visible only in scans could explain persistent swelling.
“Scans tell us what’s broken – exams show how it affects daily life.”
Predicting Recovery Timelines Accurately
Healing phases correlate directly with initial damage severity. Mild sprains might need 4-6 weeks of rest, while complex repairs could require 9+ months of rehab. Regular scan updates help adjust timelines as the body heals.
| Damage Level | Typical Treatment | Average Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 | Physical therapy | 3-6 weeks |
| Grade 2 | Bracing + rehab | 2-4 months |
| Grade 3 | Surgical repair | 6-12 months |
Recent cases show this dual approach’s power. One athlete’s normal physical exam hid a partial tear visible only through advanced imaging. Early detection prevented career-ending damage through timely intervention.
Wrapping Up Our Insights on Knee MRI and Ligament Health
Navigating joint health challenges requires precise tools and expert analysis. Advanced imaging remains vital for mapping cartilage integrity and soft tissue conditions. Our exploration revealed how preparation protocols and specialized techniques work together to uncover hidden damage.
These detailed scans empower medical teams to craft personalized treatment strategies. By merging imaging data with physical assessments, professionals address both structural issues and functional needs. This dual approach improves outcomes for chronic conditions and acute injuries alike.
We recommend consulting specialists who prioritize comprehensive evaluations. Patients benefit most when scan results inform every phase of care – from initial diagnosis to recovery milestones. Modern methods excel at tracking tissue healing and cartilage changes over time.
For complex conditions or persistent discomfort, seek providers using cutting-edge protocols. Our team combines technical expertise with compassionate guidance to optimize your joint health journey. Reach out to discuss imaging options tailored to your unique needs.
